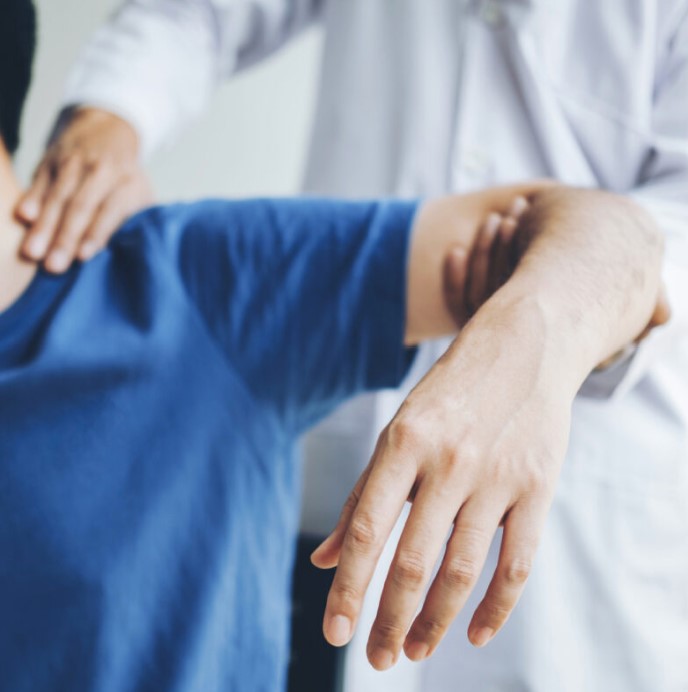
SHOULDER PAIN:
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR:
A tear in the tissues connecting muscle to bone (tendons) around the shoulder joint. A rotator cuff tear often occurs in people who repeatedly perform the same shoulder motions. Symptoms include shoulder pain and weakness. Treatment includes rest, medication, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, and possibly surgery.
TENDONITIS/BURSITIS:
Shoulder bursitis and tendinitis are common causes of shoulder pain and stiffness. Tendinitis occurs as a result of sports injuries, by repetitive minor impact on the affected area, or from a sudden, more serious injury.
OSTEOARTHRITIS/DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE:
In shoulder osteoarthritis, your cartilage and other joint tissues gradually break down. Friction in the joint increases, pain increases and you slowly lose mobility and function. Shoulder OA is not as common as OA of the hip or knee, but it is estimated that nearly 1 in 3 people over the age of 60 have shoulder OA to some degree.
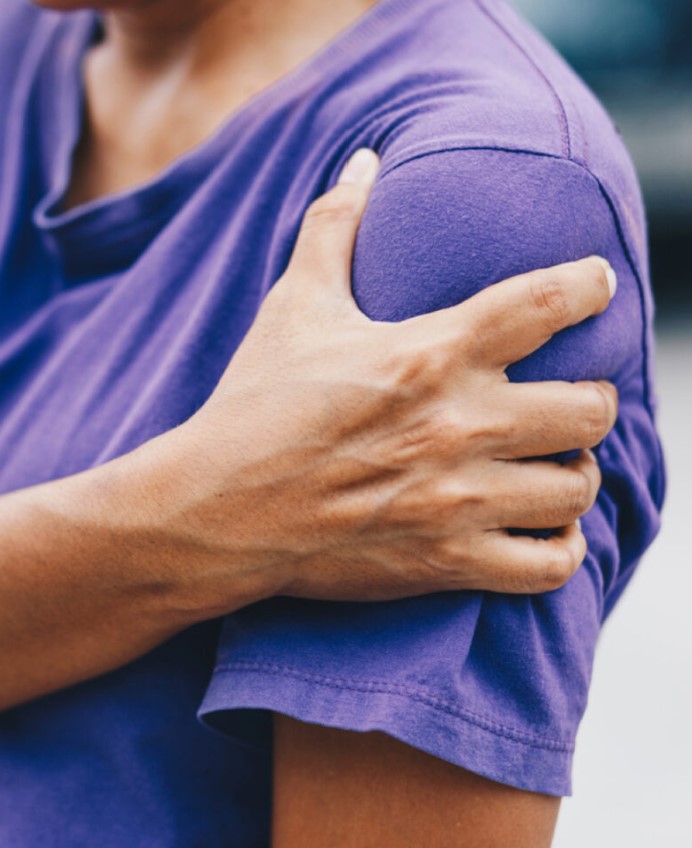

LABRAL TEAR:
- The shoulder labrum is a thick piece of tissue attached to the rim of the shoulder socket that helps keep the ball of the joint in place. The labrum can tear a few different ways:
- Completely off the bone
- Within or along the edge of the labrum
- Where the bicep tendon attaches.
LAXITY OF TENDONS AND LIGAMENTS:
Multidirectional Instability refers to a laxity of the shoulder joint with associated instability. The instability generally results from stretching of the shoulder’s supporting ligaments, which leads to increased movement of the glenohumeral joint.
ACROMIOCLAVICULAR (AC) JOINT SEPARATION/SPRAIN:
An AC joint separation, often called a shoulder separation, is a dislocation of the clavicle from the acromion. This injury is usually caused by a blow to the shoulder, or a fall in which the individual lands directly on the shoulder or an outstretched arm.
TYPES OF SHOULDER PAIN
- Acute injury
- Referred pain
CAUSES OF SHOULDER PAIN
- Rotator cuff tear
- Osteoarthritis
- SLAP tear (bicep tendon to glenoid labrum)
- Laxity of tendons and ligaments
- Bursitis causes pain and increases likelihood of a rotator cuff tear
- Fracture, dislocation, or acromioclavicular (AC) separation of the spine, shoulder, or spine
- Inflammation of the traps, neck, or bicep tendon
- Glenoid dysplasia
- Shoulder impingement
- Peripheral artery or vascular disease
- Adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
SYMPTOMS OF SHOULDER PAIN
- Generalized arm and shoulder weakness
- Numbness, or tingling (most notably in the bicep, fingers or trapezius muscle)
- Visible deformity such as one shoulder drooping below the other
- Difficulty raising arm above the head and general arm immobility
- Mechanical pain
- Discomfort such as a grinding, grating, popping, or burning sensation